The Washingtons of Wessyngton Plantation reviewed in Nashville City Paper by Todd Dills. Click here to see review.
Archive for the ‘Interviews’ Category
Author Shows History Begins at Home
Thursday, March 4th, 2010Washingtons of Wessyngton Plantation: Stories of My Family’s Journey to Freedom – Resource for Educators and Teachers
Tuesday, February 9th, 2010The Washingtons of Wessyngton Plantation: Stories of My Family’s Journey to Freedom has been released in trade paperback and is an excellent resource for teachers and educators. The book chronicles the African American experience from slavery to freedom. It has more than 100 photographs and portraits of African Americans who were once enslaved. The book covers many aspects of plantation slavery, the Civil War, Reconstruction, Jim Crow, Genealogy, and DNA testing.
http://books.simonandschuster.net/Washingtons-of-Wessyngton-Plantation/John-F-Baker-Jr/9781416567417
Battle of the Alamo Has Ties to Wessyngton Plantation
Saturday, December 26th, 2009The history of the Alamo is an important part of American history and American lore. Joseph George Washington was a participant in the defense of the Alamo.
Joseph was the son of Andrew Washington, brother of Joseph Washington, who founded Wessyngton Plantation. He was born in 1808 and lived in Robertson County, Tennessee. Joseph was described as a striking, tall figure, about six feet high, tolerably stout build, tolerably dark complexion, dark eyes and dark hair.
In 1833, Joseph George sold his uncle a slave Joe. In December of 1835, he sold three more slaves to his brother Richard Washington for $830, before he travelled west to Texas. We do not know why Joseph joined in the fight for the Alamo. It could have been that the Republic of Texas offered land to men who helped win its independence from Mexico. Another reason could have been he was seeking an adventure as he went with other young men from Tennessee and nearby Kentucky.
In 1836, during the 12 day siege by Mexican troops under the command of Santa Anna, Joseph George Washington was killed. Within the Washington family and Alamo lore he became known as “Alamo Joe.”
Nat Turner’s Rebellion of 1831
Monday, December 21st, 2009In 1831, Nat Turner led the largest slave rebellion in the history of the United States. Turner, born in 1800 in Jerusalem, Southampton County, Virginia. Wessyngton Plantation’s founder Joseph Washington lived in Southampton County before he came to Tennessee. Many of the slaves on Wessyngton Plantation were brought by Joseph to Tennessee.
In Virginia, Turner, a self-proclaimed Baptist minister, was known as “The Prophet” to the enslaved African Americans and often conducted services for them. He claimed to be given visions by God, and that he was ordained to lead his people to freedom. Unlike most slaves and many whites, Turner was able to read and write.
Turner’s group of followers was composed of more than 50 fellow slaves and free blacks. During the insurrection of 1831, the group went through the countryside of Southampton County killing 55 men, women, and children. The insurrection lasted for two days before the local militia put it down. Turner and several of the leaders were executed; others were transported out of the area.
The Turner rebellion put fear in the hearts and minds of slave holders throughout the South, which led to laws further restricting the activities of enslaved African Americans and free blacks.
The revolt influenced the Tennessee legislature to pass laws in 1831 that prevented more free blacks from entering the state. Any person emancipating a slave had to send him out of the state. When the new constitution in Tennessee was written in 1834, free blacks were denied voting privileges.
Washingtons of Wessyngton Plantation Presented to Gateview Elementary School Students in Portland, Tennessee
Monday, November 30th, 2009On November 20th I had the honor of delivering a presentation about my book The Washingtons of Wessyngton Plantation to the entire fifth grade class at Gateview Elementary School in Portland, Tennessee. More than 100 students attended. Prior to my visit the students had studied the Civil War, which tied into my program. The students were very attentive and had many questions. Following the presentation many of the students expressed an interest in tracing their genealogy.
Dred Scott Decision: Impact on African American Citizenship in the United States
Tuesday, November 24th, 2009
In 1847 an enslaved African American, Dred Scott, went to trial to sue for his freedom. This case, which later became known as Dred Scott v. Sanford, impacted the citizenship of all African Americans throughout the United States.
Dred Scott was born a slave in Southampton County, Virginia and was owned by Peter Blow. Peter Blow was the great-nephew of Colonel Michael Blow who owned my ancestors before they were brought to Wessyngton Plantation by Joseph Washington.
Scott was taken to Alabama by the Blow family and later to St. Louis. After Peter Blow’s death in 1832, Scott was bought by an army surgeon Dr. John Emerson who took him to Illinois and the Wisconsin Territory.
Scott’s stay in Illinois and Wisconsin, where slavery was prohibited, gave him the legal standing to make a claim for his freedom. The abolitionists encouraged him to sue for his freedom. The case and appeals took ten years. In March 1857, the United States Supreme Court declared that all blacks, slaves as well as free blacks, were not, and could never become, citizens of the United States.
The decision was a victory for southern slaveholders, while northerners were outraged at its outcome. The Dred Scott case influenced the nomination of Abraham Lincoln to the Republican Party and his election that led to the South’s secession from the Union and ultimately the freedom of all African Americans.
Peter Blow’s sons, who had grown up with Dred Scott, helped him pay the legal fees for his lengthy case. After the Supreme Court’s decision, they purchased Scott and his wife and then emancipated them.
Dred Scott died nine months later—a free man.
.
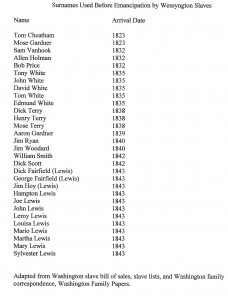
Use of Surnames Among African Americans Before Emanicaption
Tuesday, November 10th, 2009Slaves were usually known by their first names, especially on small farms with few slaves. Plantation owners rarely recorded their slaves with surnames unless they had several individuals with the same first names. For that reason the use of surnames by slaves was far more common on large plantations where more people were likely to have the same given names.
Due to Wessyngton Plantation having such a large enslaved population many African Americans are listed with their previous owners’ surnames as early as the 1820s.
Slave bills of sale and other documents in the Washington Family Papers collection details the origins of many of these African American families.
The list above documents the names African Americans on Wessyngton Plantation who used surnames prior to emancipation and the date of their arrival on the plantation.
International Black Genealogy Summit in Ft. Wayne, Indiana
Sunday, November 8th, 2009I just returned from a very exciting event—The first International Black Genealogy Summit held in Ft. Wayne, Indiana on October 29-31, 2009. Several hundred people participated. Throughout the conference I shared my research experience with genealogists. It was wonderful to speak with many people who had already read my book. The give and take of ideas illustrates that we are just at the beginning of a long and interesting journey to learn about our roots.
At the Meet the Authors event everyone could talk to the authors of books related to African American genealogy. The authors posed together for this photo. (L-R) Tony Burroughs who wrote Black Roots: A Beginners Guide To Tracing the African American Family Tree; myself; Tim Pinnick, author of Finding and Using African American Newspapers; and (Seated) Frazine Taylor, with her book Researching African American Genealogy in Alabama.